Comprehensive Eye Testing
During your eye examination, the doctor may detect findings related to the health of your eyes that require further evaluation. It is the doctor’s role to leave no stone unturned when it comes to the health of your eyes. Fortunately, our clinics are equipped with cutting edge diagnostic instruments capable of the early detection of a vast array of eye diseases and conditions. Here we will list some of the equipment we use to ensure you receive the most thorough diagnostic and treatment procedures available.
For more information, please on the links below:
OPTOMAP
The Optomap Retinal Exam non-invasively captures an instantaneous, ultra-widefield digital scan of the retina, revealing important information for the comprehensive evaluation of systemic and ocular health. The 200-degree internal scan is captured in a quarter of a second. The Optomap is truly a revolution in ocular photography. The only other way to see as much of the internal anatomy of the eye is to dilate the pupil.
The Optomap also has powerful tools for isolating different layers of the inside wall of the eye, which can be critical in diagnosing tumors and cancers. It has the ability to help the doctor detect holes, tears, and detachments of the retina. Because it uses two different colors of laser to scan the retina, vascular leakages caused by diabetes and hypertension are much easier to see.
One of the most rewarding aspects of an optomap exam is that the doctor will go over it with you in the exam room. Your doctor will pull the images up right in front of you and explain each detail. You will see a part of your body you have never seen before. And since all the images are securely stored on a digital server (which is backed up daily) your doctor will have the ability to review and compare the images to any changes that may occur in the future.
CIRRUS OCT
The retina lines the inner wall of the eye. It is the job of the retina to transform the light that is focused into the eye into an electrical signal that can be processed by the brain. The retina is an unbelievably complex structure, consisting of ten layers and dozens of different types of cells. In being such a complicated system there are numerous diseases and abnormalities that may affect its function.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive diagnostic instrument used for high-resolution imaging of the individual layers of the retina. It has the ability to detect a vast array of problems in the eye, often prior to any symptoms being present. With an OCT, doctors are able to see a cross-section or 3D image of the retina and detect the early onset of a variety of eye conditions and eye diseases such as macular degeneration, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy (the top three diseases known to cause blindness).

The OCT allows for detection of other diseases such as macular holes, hypertensive retinopathy, and even optic nerve damage. OCT can pick up subtle changes in the central retina (macula), sometimes even before these changes are visible with any other method of examination. This is very useful in monitoring the retina of patients on medications such as Plaquenil, or hydroxychloroquine. Using an OCT allows for early treatment and dramatically improves the success of these treatments, especially in diseases such as wet macular degeneration – where the eye disease progresses rapidly. OCT is quickly becoming the standard of care for the diagnosis and treatment of retinal anomalies. At Family Eye Clinic we have the newest OCT technology in order to help us preserve your vision.

VISUAL FIELD TESTING
Normally we perceive a wide area of the space in front of us. Without moving our eyes, we see not only what is straight ahead, but some of what is above, below and off to either side. Most people are familiar with this as “peripheral vision.” The entire area which we see is known as the visual field
Our vision is the sharpest in the dead center of the visual field. That is why we turn our eyes toward objects that we want to see better. The further away from the center of our vision, an object is, the less clearly we can see it. When an object moves far enough to the side, it disappears from our vision completely.
The size, shape, and sensitivity of our visual field are very informative. Using special equipment the doctor will measure how far up, down, left, and right the eye sees without moving, as well as the sensitivity to light in different sections of the visual field. This can tell the doctor many things about the retina, optic nerve, visual pathway through the brain, and visual cortex. There are well-known patterns in the test results that help doctors recognize certain types of injury or disease. Brain abnormalities such as those caused by strokes or tumors can affect the visual field. In fact, the location of the stroke or tumor in the brain can frequently be determined by the size, shape, and site of the visual field defect. By giving more visual field tests at regular intervals, doctors can also tell whether a condition is getting better or worse.
The mapping of the visual field is being done by a computerized machine called the Humphrey Field Analyzer. This machine is one of the best methods to measure the visual field. The testing is not difficult. Since this exam draws a map of your vision, it is important that you hold your eye still and look straight ahead at all times. Inside the machine, there is a steady yellow light for you to look at. Unless told otherwise, you should stare at this light at all times. The test lights will flash on and off at different times and different places within the machine. You will be given a response button to hold. You should press the button whenever you think you have seen a light flash. The best time to blink is right after you have pushed the button. Some lights will be bright and some will be dim. Some of the lights will be too dim to be seen. There will be periods of time when you will not see anything. Don’t be alarmed by this. The machine purposely makes some of the lights too dim. This will measure how sensitive your eye is in different areas.
During the exam, you will hear a range of noises as the light projector moves and the shutter opens and closes. Try to ignore these noises and respond only to the lights. At times, the machine tests your responses by either not projecting any lights (to see if you are responding to the noises) or projecting very bright lights (to see if you are paying attention).
This exam can take up to 10 minutes for each eye. It is very important that you be seated comfortably with your forehead pushed forward into the machine as far as possible. You should feel relaxed with no pressure in your shoulders or neck. The light should be clearly in focus. You should let the technician know right away if you are not comfortable or if the light is not in focus. If you wish to rest during the exam, hold down the response button. The machine will beep and alert the technician to pause the test.
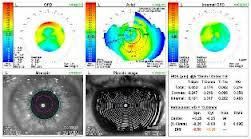
CORNEAL TOPOGRAPHY
When we look someone in the eye we see the color of their eye, the iris. But in front of the iris is a clear tissue which makes up the outermost aspect of the eyeball, known as the cornea. The cornea an extremely important element in the eye because it is the first structure that light passes through on its way to the retina. It is responsible for ⅓ of the focusing power of the eye. In order to keep this focus sharp, the cornea must have a very organized internal structure and a very uniform smooth exterior and interior surface.
There are many variations that occur with the shape or curvature of the cornea. By analyzing these variations the doctor is able to determine what will be the best treatment option to produce the clearest, sharpest vision. To measure the corneal shape and curvature the doctor will use an instrument called a corneal topographer. The topographer uses waves of light to measure detailed parameters at over 2,500 points on the surface of the cornea. Using this data your doctor will be able to find corneal dystrophies, degenerations, and diseases that are otherwise undetectable. The data also allows your doctor to select a contact lens that precisely fits the curvature of the eye. Providing the most comfortably fitting, clearest options for contact lenses.
ABBERROMETER
The optical system of the eye is not perfect. During an eye examination, the doctor will ask questions and perform testing in an attempt to get the optical system of the eye to focus very clearly. However, there are many imperfections in the tissues and structures of the eye which cause distortions and aberrations in the way that light gets focused onto the retina. The doctor will use an aberrometer to measure these distortions. Although each type of aberration may be small, when all added together they can have a dramatic effect on the clarity of vision. Knowing the amount and location of the aberrations within the optical system lets the doctor make changes to the prescription of glasses or contacts which can provide a clearer vision than ever before possible.
Wavefront aberrometry is also used during LASIK. The aberration pattern captured is unique in every person, much like your fingerprint. By mapping the aberrations specific to your eye, the doctors are able to formulate a custom ablation (wavefront, high definition) LASIK treatment profile. This allows the laser to correct all of the tiny imperfections in your optical system. Thanks to the advancements in wavefront aberrometry, the laser will produce high definition vision, often sharper than you ever had with glasses or contacts.

SPECULAR MICROSCOPY
The cornea is the clear part of the very front of the eye. It consists of five layers that each has a special role in maintaining the optical clarity of the tissue. The very innermost layer is called the endothelium. The endothelium is only a single cell thick. These cells are hexagonal and arranged in a honeycomb pattern. It is the duty of the endothelial cells to pump fluid out of the upper layers of the cornea. Without this, the cornea will swell, which can lead to numerous problems including fluctuations in the clarity of vision, severe pain, eventual corneal decompensation requiring a corneal transplant.
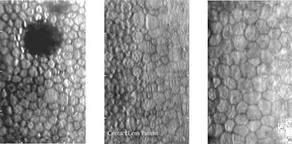
The body does not produce endothelial cells, we are born with all the endothelial cells that we will ever have. Throughout life, we normally lose some of our endothelial cells. However, if we lose too many due to disease or injury, a lot of problems may occur. When there are indications that the endothelial tissue may be compromised the doctor will use a special device known as a specular microscope. This instrument provides a very detailed analysis of the shape, size, and number of endothelial cells. Using this information the doctor can decide the best course of action, be it medications or surgery.
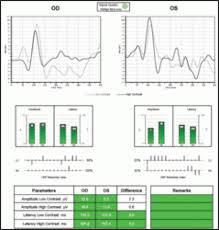
VISUALLY EVOKED POTENTIAL
When light strikes the retina it is converted into an electrical signal and sent into the brain. Visually Evoked Potential (VEP) tests measure the electrical activity in the areas of the brain that process this visual signal. VEPs are used primarily to measure the functional integrity of the visual pathways from the retina via the optic nerves to the visual cortex of the brain. VEPs better quantify functional integrity of the optic pathways than scanning techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

These tests are often used to assist in the diagnosis of optic nerve diseases, such as optic neuritis and glaucoma. Any abnormality that affects the visual pathways or visual cortex in the brain can affect the VEP. Examples are cortical blindness due to meningitis or anoxia, optic neuritis as a consequence of demyelination, optic atrophy, stroke, compression of the optic pathways by tumors, amblyopia, and neurofibromatosis. They are also useful in detecting and treating multiple sclerosis. In general, myelin plaques common in multiple sclerosis slow the speed of VEP wave peaks Many times VEP can indicate problems along the pathways of certain nerves that are too subtle to be noticed or found on a doctor's exam.
For more information, please click on the links below.
Diopsys-NOVA-Patient-Brochure
BLOOD SUGAR SCREENING
Diabetes affects millions of Americans and is the leading cause of blindness in the U.S. One of the most common symptoms of abnormal blood sugar is blurred vision. If the doctor suspects that blood sugar levels could be a problem, a blood sugar screening will be done in the office.